Ensuring the security of your digital assets through robust API authentication is non-negotiable in today’s fast-evolving software landscape. For QA managers, SDETs, and testing professionals, mastering API authentication methods is vital to protecting sensitive data and preventing breaches. This comprehensive guide dives straight into the top 10 API authentication types used across industries in 2025—arming you with real examples, tool insights, actionable best practices, and forward-looking trends pivotal for your testing and DevOps strategies.
Why API Authentication Matters for QA Professionals
In the age of microservices, app integrations, and decentralized architectures, APIs have become the backbone of critical business processes. A staggering 83% of enterprises reported API-related security incidents in recent industry surveys, underscoring the risk unprotected or improperly tested APIs pose to sensitive user data and application stability. Without effective authentication mechanisms, unauthorized access and data leaks become alarmingly easy.
QA teams must understand API authentication deeply, not just for security but also for ensuring functional correctness, seamless integrations, and compliance with regulatory standards.
The Top 10 API Authentication Methods in 2025
| Authentication Type | Best For | Key Strength | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|---|
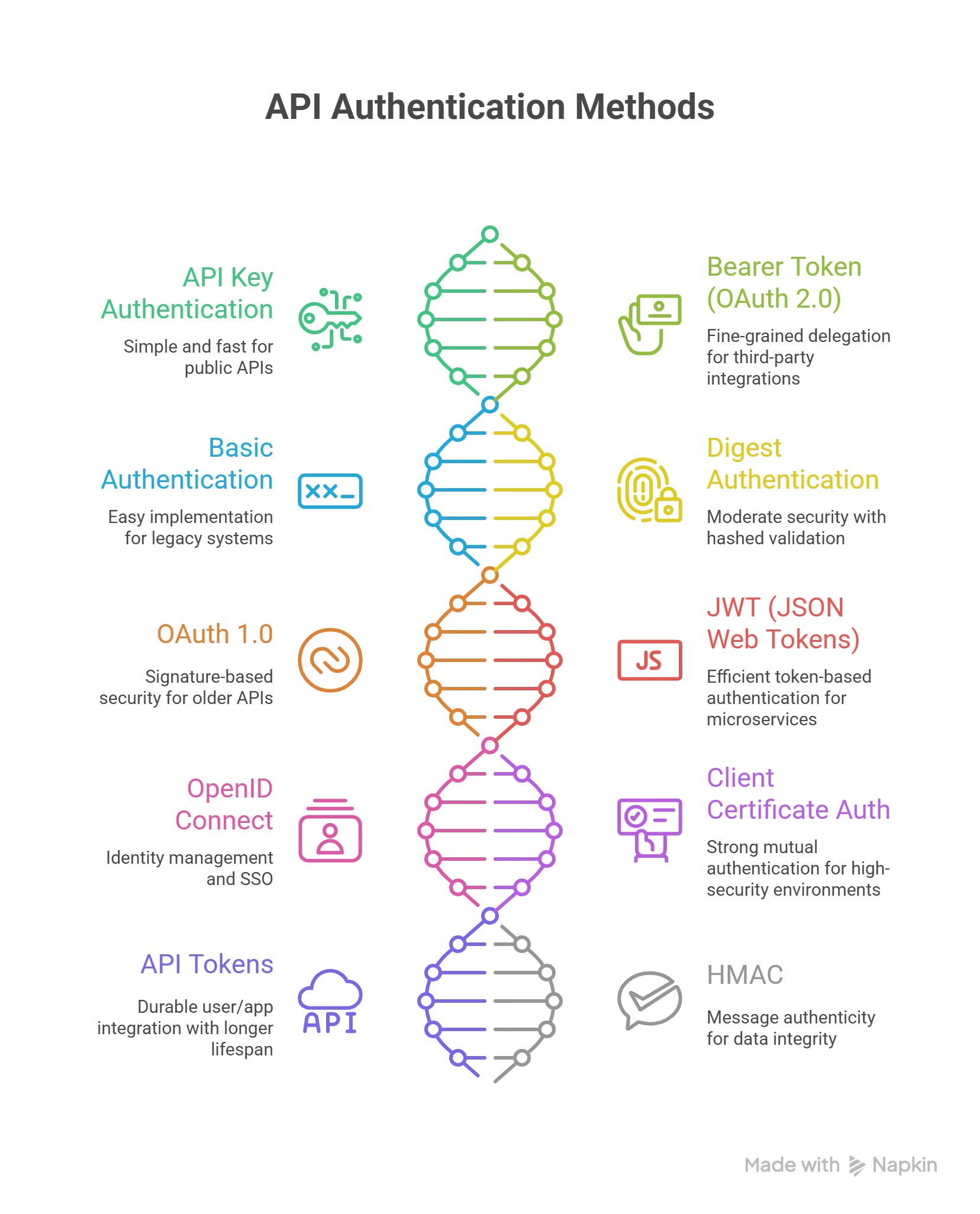
| API Key Authentication | Simple public/internal APIs | Easy integration / Fast | Weather apps fetching data via API key |
| Bearer Token (OAuth 2.0) | Third-party integrations | Fine-grained delegation | Mobile apps accessing Google Calendar |
| Basic Authentication | Legacy/internal systems | Simple to implement | Internal dashboards with username/password |
| Digest Authentication | Moderate security needs | Hashed validation | Email clients hash passwords before transmission |
| OAuth 1.0 | Legacy APIs | Signature-based security | Older social media platforms |
| JWT (JSON Web Tokens) | Stateless microservices/SO | Efficient token-based | Web apps issuing JWTs to users |
| OpenID Connect | Identity management & SSO | Identity & auth combined | Single sign-on for enterprise portals |
| Client Certificate Auth | High-security environments | Strong mutual authentication | Corporate VPNs requiring client certs |
| API Tokens | Durable user/app integration | Longer lifespan tokens | E-commerce third-party app authorizations |
| HMAC | Data integrity critical apps | Message authenticity | Cloud storage validating data using HMAC |
Real-World Use Cases and Tool Insights
1. API Key Authentication
Used widely for simple integrations, API keys are easy to implement but lack fine-grained security controls. For instance, Stripe and OpenWeather provide API keys to allow developers quick access to their services without complex auth flows. However, key leakage poses a risk, making best practices around key storage and rotation critical.
2. Bearer Token Authentication (OAuth 2.0)
OAuth 2.0 reigns supreme in controlling delegated access for third-party apps. For example, mobile apps that access Google Calendar or Microsoft Graph API embed bearer tokens in requests. Popular testing tools like Postman support OAuth 2.0 flows, ensuring token validation and refreshing can be simulated effectively during QA.
3. Basic Authentication
Still used in legacy systems, basic auth transmits user credentials encoded but not encrypted—requiring HTTPS for security. QA teams validating basic auth should test for proper error responses and secure transmission failures.
4. Digest Authentication
Improves over basic auth by sending hashed credentials, common in legacy email clients. QA engineers need to validate the hashing algorithms and ensure secure nonce generation.
5. OAuth 1.0
Though largely replaced by OAuth 2.0, OAuth 1.0 is present in older social media APIs. Testing here involves signature verification and timestamp validation.
6. JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
JWTs provide stateless authentication with claims sent in compact tokens. Used in modern microservices architectures, a QA workflow should include signature verification, expiration handling, and claim validation. Tools like JWT.io help decode and verify tokens manually.
7. OpenID Connect
Enriches OAuth 2.0 by adding an identity layer, enabling single sign-on experiences. QA must confirm proper flow authorization, token introspection, and user info endpoint validation. It’s popular in enterprise portals.
8. Client Certificate Authentication
Used in sensitive environments, mutual TLS ensures client-device authenticity. QA involves certificate validation, expiry checks, and revocation tests primarily seen in corporate VPNs and banking apps.
9. API Tokens
These tokens have longer lifespans and are scoped to user or app identities. QA focus includes token lifecycle and scope validation, common in e-commerce integrations and SaaS vendor APIs.
10. HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code)
Essential for ensuring integrity and authenticity, HMAC involves hashing request data with a secret key. QA should validate signature correctness and replay attack resistance. Cloud platforms like AWS S3 use HMAC extensively.
Market Growth and Industry Trends
The API security market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 28% from 2024 to 2030, driven by escalating API adoption across organizations and rising cybersecurity threats. Emerging trends include passwordless authentication, AI-powered anomaly detection, and zero trust security architectures focusing on continuous verification beyond initial authentication.
For QA teams, this translates to evolving roles incorporating security testing, automation of authentication flows, and usage of advanced security testing platforms like Pynt and OWASP ZAP.
Tool Comparison: Top API Authentication Testing Solutions
| Tool | Strengths | Weaknesses | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pynt | CI/CD integration, Business logic testing | Newer, smaller ecosystem | DevSecOps & automated API security |
| OWASP ZAP | Open-source, extensive plugins | Manual testing focus | Security validation & penetration testing |
| Postman | User-friendly, supports OAuth 2.0 flow | Limited vulnerability testing | Functional and OAuth testing |
| SoapUI Pro | Rich API testing suite | Paid license required | Enterprise functional & security testing |
| JMeter | Performance & load testing | Complex setup for beginners | API load & performance testing |
Best Practices for QA: API Authentication Testing
- Automate authentication tests in CI/CD pipelines to catch regressions early.
- Validate errors for unauthorized and forbidden responses (401, 403).
- Test token expiry, refresh mechanisms, and role-based access controls.
- Perform negative testing using invalid, expired, or tampered tokens.
- Use tools supporting OAuth flows and JWT validation.
- Ensure HTTPS is enforced for all tokens and credentials transmission.
- Review API documentation against actual header and parameter behaviors.
- Monitor logs for unusual authentication failures and retry patterns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is API authentication and why does it matter?
API authentication confirms the identity of users or systems to protect sensitive data and ensure only authorized access. - How does API Key Authentication differ from OAuth 2.0?
API keys are simple static tokens, while OAuth 2.0 provides a secure token-based, delegated access mechanism with expiry and scopes. - What is the ROI of implementing strong API authentication?
Investing in robust authentication reduces data breaches, ensures compliance, and builds user trust, lowering incident costs and downtime. - Who should implement OAuth 2.0?
Organizations requiring third-party integration and fine-grained access controls benefit most from OAuth 2.0. - What common challenges occur during implementation?
Token expiration handling, scope misconfigurations, and secure token storage often present pitfalls. - What future trends affect API authentication?
AI-driven anomaly detection, zero trust policies, and passwordless authentication are reshaping API security. - How should QA get started testing API authentication?
Understand authentication flows, automate scenarios in tools like Postman, and validate both happy and error paths. - Are there platform-specific considerations?
Yes, for example, AWS uses HMAC extensively, Google APIs prefer OAuth 2.0, requiring tailored token handling. - What about securing tokens in transit?
Always use HTTPS/TLS to encrypt tokens and credentials during communication to prevent interception. - How can SDETs integrate API authentication testing into CI/CD?
Use automated security testing tools that embed authentication flows, enabling tests on every build and deployment.
Actionable Next Steps
- Audit all your APIs to identify the current authentication methods in use.
- Gradually migrate to token-based or certificate-based authentication where possible.
- Integrate automated API security testing tools like Pynt and OWASP ZAP in your CI/CD pipelines.
- Stay updated with evolving API security trends and standards to future-proof your QA strategy.
🔥 Level Up Your SDET Skills 🔥
Monthly Drop : Real-world automation • Advanced interview strategies • Members-only resources
