Generative AI pulls creativity, efficiency, and innovation out of its digital hat! Generative AI generates text that reads like Shakespeare. It also creates jaw-dropping art. Additionally, it compresses data like a pro. Generative AI is transforming industries at lightning speed. Today, we’ll explore three key players in this magical space. They are LLMs (Large Language Models), GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), and VAEs (Variational Autoencoders). Let’s decode the brilliance behind these models, with tools and examples to bring them to life!
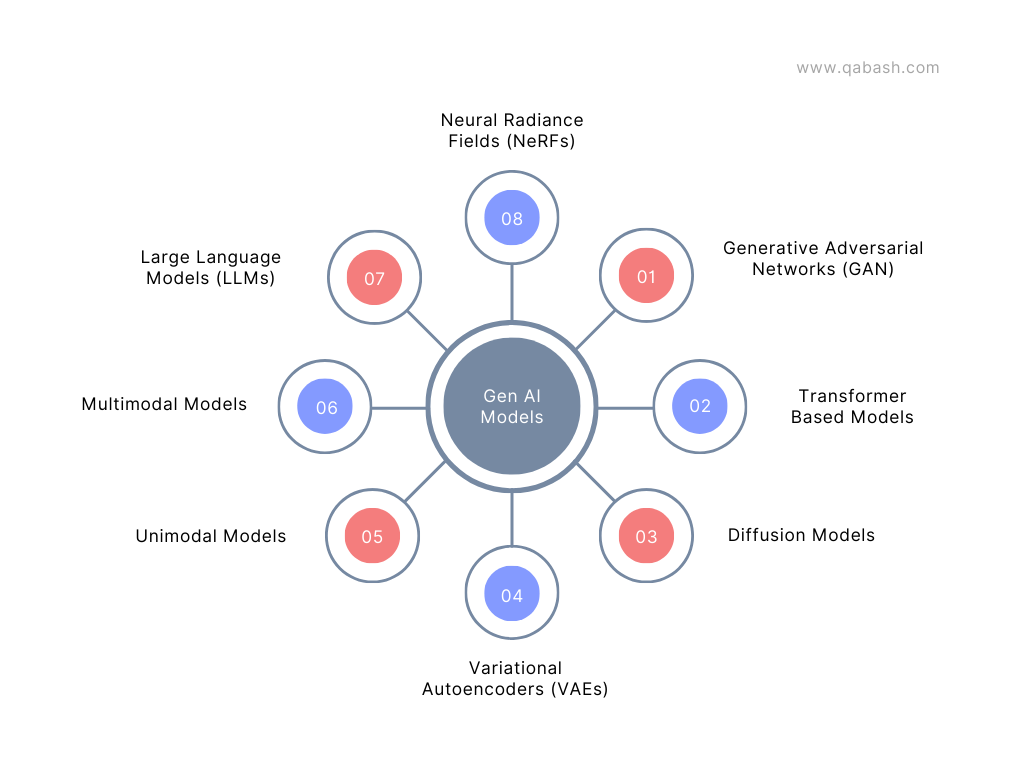
What Are Generative AI Models? 🧩
Generative AI models are algorithms designed to create new data similar to existing data. Think of them as highly skilled chefs who can whip up a perfect replica of a dish just by tasting it once. Whether it’s text, images, code, or even synthetic datasets, these models generate outputs that mimic human creation.
Here are the three stars of the show:
- LLMs (Large Language Models): Masters of text and code.
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks): The artists and deepfake creators.
- VAEs (Variational Autoencoders): The data compression and synthetic data geniuses.
1. LLMs: The Wordsmiths and Coders of AI 🖋
What Are LLMs?
LLMs are neural networks trained on massive amounts of text to understand and generate human-like language. They’re used for a variety of tasks: writing essays, summarizing articles, answering questions, translating languages, and even generating code!
Tools Powered by LLMs:
- ChatGPT: A conversational AI that can chat, write articles, and help debug code.
- GitHub Copilot: Your coding buddy, suggesting lines of code as you type.
- Bard by Google (now Gemini) : A competitor in conversational AI that focuses on search-oriented answers.
Real-World Use Cases:
- Customer Support: AI chatbots powered by LLMs handle queries 24/7.
- Content Creation: Bloggers and marketers use tools like Jasper to write faster.
- Code Assistance: Developers speed up coding with tools like Tabnine.
| Feature | Use Case | Example Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Text generation | Blog writing | Jasper |
| Code generation | Developer assistance | GitHub Copilot |
| Question answering | Virtual assistants | ChatGPT |
2. GANs: The Picasso of AI 🎨
What Are GANs?
GANs consist of two neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—playing a game of cat and mouse. The generator creates fake data (images, videos, etc.), while the discriminator evaluates its authenticity. Over time, the generator gets better at creating realistic outputs.
Tools Powered by GANs:
- DALL•E 3: Generates stunning images from textual descriptions.
- DeepArt.io: Turns photos into artwork inspired by famous painters.
- DeepfakeLab: Creates deepfake videos by swapping faces.
Real-World Use Cases:
- Art and Design: Generating unique artwork or enhancing creative projects.
- Gaming: Creating realistic characters and environments.
- Entertainment: Producing deepfake videos for fun or storytelling.
| Feature | Use Case | Example Tool |
| Image generation | Digital art creation | DALL•E 2 |
| Deepfake creation | Entertainment | DeepfakeLab |
| Style transfer | Artistic photo editing | DeepArt.io |
3. VAEs: The Data Alchemists 🧠
What Are VAEs?
VAEs compress data into smaller representations and then reconstruct it with minimal loss. They’re ideal for creating synthetic datasets, improving data efficiency, and handling high-dimensional data.
Tools Powered by VAEs:
- DataSynth: Generates synthetic datasets for testing and analysis.
- TensorFlow VAEs: A framework for implementing custom VAE models.
- Synthesia: Combines VAEs and GANs to create synthetic media.
Real-World Use Cases:
- Synthetic Data Generation: Creating data for testing without compromising privacy.
- Anomaly Detection: Spotting outliers in datasets.
- Data Compression: Efficiently storing large datasets.
| Feature | Use Case | Example Tool |
| Data compression | Storage optimization | TensorFlow VAEs |
| Synthetic data creation | Privacy-preserving AI | DataSynth |
| Anomaly detection | Fraud detection | Custom VAEs |
How These Models Complement Each Other 🔄
While each model shines in its domain, they often work together to solve complex problems. For example:
- An LLM can describe an image generated by a GAN.
- A VAE can compress GAN-generated data for efficient storage.
| Model | Strength | Example Collaboration |
| LLM | Text and code generation | Describing GAN-generated images |
| GAN | Visual content creation | Generating data for VAE compression |
| VAE | Data optimization | Enhancing GAN data storage |
The Fun (and Ethical) Side of Generative AI 😉
Generative AI isn’t all work and no play. It’s behind fun apps like Reface and FaceApp, creating hilarious transformations. But with great power comes great responsibility. Ethical considerations like preventing misuse in deepfakes or ensuring data privacy are critical.
Conclusion: Generative AI Is the Future 🌐
Generative AI models like LLMs, GANs, and VAEs are reshaping industries by unlocking creative, efficient, and innovative possibilities. From generating art to simplifying code and producing synthetic data, the potential is endless. Understanding these tools not only keeps you ahead of the curve but also opens doors to exciting new applications.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between GANs and VAEs?
GANs focus on generating realistic outputs, while VAEs excel at compressing data and generating synthetic datasets.
2. Can I use LLMs without coding experience?
Yes! Tools like ChatGPT and Jasper are user-friendly and require no coding knowledge.
3. Are these tools free?
Many tools offer free versions with limited features, while premium versions unlock full capabilities.
4. What industries benefit from these models?
Industries like healthcare, entertainment, e-commerce, and education leverage generative AI for diverse applications.
5. How can I start using these tools?
Explore beginner-friendly tools like ChatGPT, DALL•E 3, and TensorFlow tutorials to get started.
QABash Nexus—Subscribe before It’s too late!
Monthly Drop- Unreleased resources, pro career moves, and community exclusives.
